Table of Contents
- Conversations Overview
- Setup
- Conversation Types
- Conversation Entries
- Using Model Tools
- Pre-processing Conversation Entry Responses
- Real-time Streaming Responses
- Limiting Conversation History
Conversations Overview
Raif provides a full-stack (models, views, & controllers) LLM chat interface with built-in streaming support.
If you use the raif_conversation view helper, it will automatically set up a chat interface that looks something like:
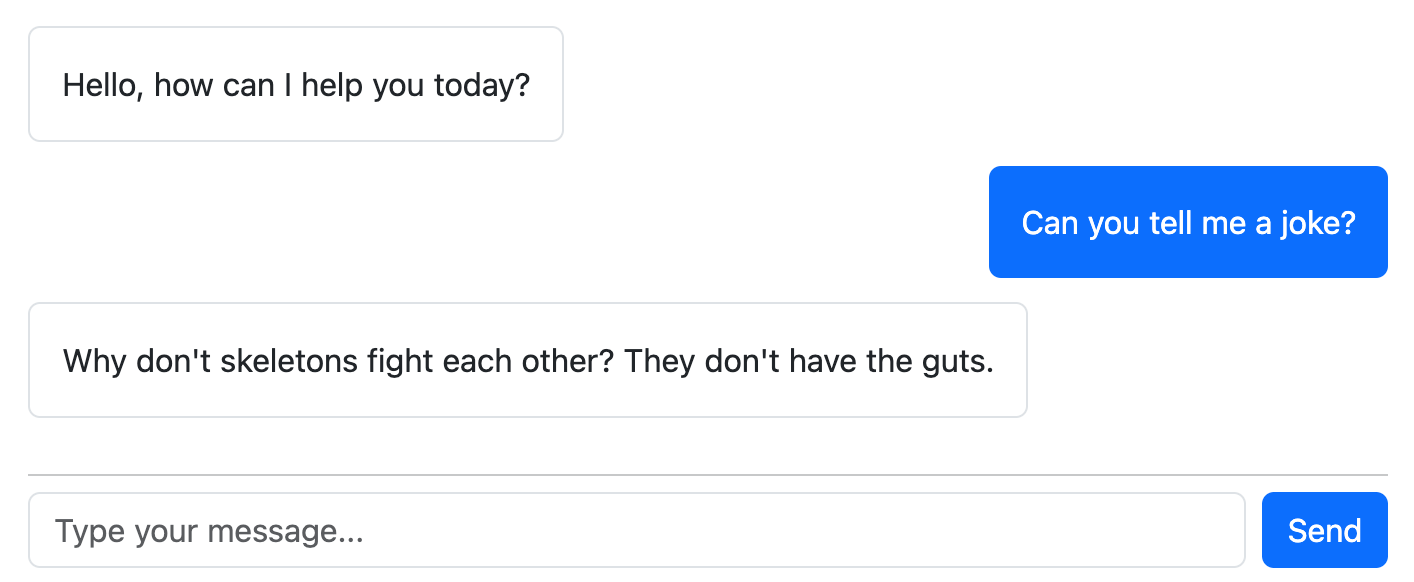
This feature utilizes Turbo Streams, Stimulus controllers, and ActiveJob, so your application must have those set up first.
Setup
First set up the css and javascript in your application. In the <head> section of your layout file:
<%= stylesheet_link_tag "raif" %>
In an app using import maps, add the following to your application.js file:
import "raif"
In your initializer, configure who can access the conversation controllers (you’ll need to restart your server for this to take effect):
Raif.configure do |config|
config.authorize_controller_action = ->{ current_user.present? }
end
In a controller serving the conversation view:
class ExampleConversationController < ApplicationController
def show
@conversation = Raif::Conversation.where(creator: current_user).order(created_at: :desc).first
if @conversation.nil?
@conversation = Raif::Conversation.new(creator: current_user)
@conversation.save!
end
end
end
And then in the view where you’d like to display the conversation interface:
<%= raif_conversation(@conversation) %>
By default, the conversation interface will use Bootstrap styles. If your app does not include Bootstrap, you can override the views to update styles.
Conversation Types
You can create custom conversation types using the generator, which gives you more control over the conversation’s system prompt, initial greeting message, and available model tools.
For example, say you are implementing a customer support chatbot in your application and want to a specialized system prompt and initial message for that conversation type:
rails generate raif:conversation CustomerSupport
This will create a new conversation type in app/models/raif/conversations/customer_support.rb.
You can then customize the system prompt, initial message, and available model tools for that conversation type:
class Raif::Conversations::CustomerSupport < Raif::Conversation
before_create ->{
self.available_model_tools = [
"Raif::ModelTools::SearchKnowledgeBase",
"Raif::ModelTools::FileSupportTicket"
]
}
before_prompt_model_for_entry_response do |entry|
# Any processing you want to do just before the model is prompted for a response to an entry
end
def system_prompt_intro
<<~PROMPT
You are a helpful assistant who specializes in customer support. You're working with a customer who is experiencing an issue with your product.
PROMPT
end
# The initial message is used to greet the user when the conversation is created.
def initial_chat_message
I18n.t("#{self.class.name.underscore.gsub("/", ".")}.initial_chat_message")
end
end
You’ll also need to add the conversation type to your initializer:
Raif.configure do |config|
config.conversation_types += [
"Raif::Conversations::CustomerSupport"
]
end
Conversation Entries
Each time the user submits a message, a Raif::ConversationEntry record is created to store the user’s message & the LLM’s response. By default, Raif will:
- Queue a
Raif::ConversationEntryJobto process the entry - Make the API call to the LLM
- Call
Raif::Conversation#process_model_response_messageon the associated conversation to pre-process the response. - Invoke any tools called by the LLM & create corresponding
Raif::ModelToolInvocationrecords - Broadcast the completed conversation entry via Turbo Streams
Using Model Tools
You can make model tools available to the LLM in your conversations by including them in the Raif::Conversation#available_model_tools array.
Here’s an example that provides Raif::ModelTools::SearchKnowledgeBase and Raif::ModelTools::FileSupportTicket tools to the LLM in our CustomerSupport conversation:
class Raif::Conversations::CustomerSupport < Raif::Conversation
before_create ->{
self.available_model_tools = [
"Raif::ModelTools::SearchKnowledgeBase",
"Raif::ModelTools::FileSupportTicket"
]
}
def system_prompt_intro
<<~PROMPT
You are a helpful assistant who specializes in customer support. You're working with a customer who is experiencing an issue with your product.
PROMPT
end
end
Displaying Model Tool Invocations in a Conversation
When you generate a new model tool, Raif will automatically create a corresponding view partial for you in app/views/raif/model_tool_invocations. The conversation interface will then use that partial to render the Raif::ModelToolInvocation record that is created when the LLM invokes your tool.
Here is an example of the LLM invoking a SuggestNewScenarios tool in a conversation and displaying it using its app/views/raif/model_tool_invocations/_suggest_new_scenarios.html.erb partial:
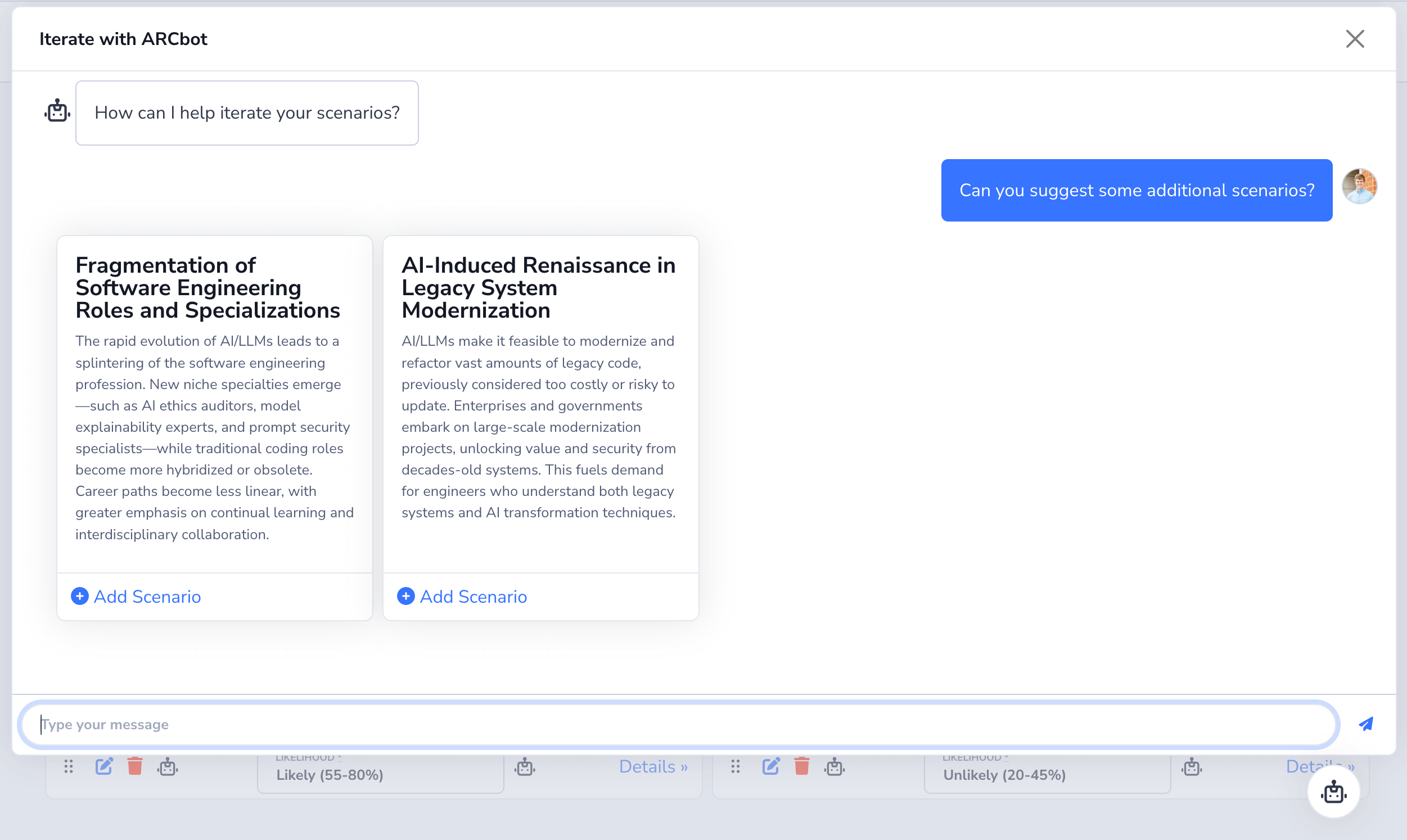
If your tool should not be displayed to the user, you can override the renderable? method in your model tool class to return false:
class Raif::ModelTools::SuggestNewScenarios < Raif::ModelTool
def renderable?
false
end
end
Providing Tool Observations/Results to the LLM
Once the tool invocation is completed (via the tool’s process_invocation method), you can provide the result back to the LLM as an observation. For example, if you’re implementing a GoogleSearch tool, you’ll want to return the search results.
You implement the observation_for_invocation method in your model tool class to control what is provided back to the LLM:
class Raif::ModelTools::GoogleSearch < Raif::ModelTool
class << self
def observation_for_invocation(tool_invocation)
JSON.pretty_generate(tool_invocation.result)
end
end
end
Pre-processing Conversation Entry Responses
You may want to manipulate the LLM’s response before it’s displayed to the user. For example, say your system prompt instructs the LLM to include citations in its response, formatted like [DocumentID 123]. You then want to replace those citations with links to the relevant documents.
You can do this by overriding the process_model_response_message method in your conversation class:
class Raif::Conversations::CustomerSupport < Raif::Conversation
def process_model_response_message(message)
message.gsub!(/\[DocumentID (\d+)\]/i, '<a href="/documents/\1">\1</a>')
end
end
This method is called after the LLM’s response is received and before it’s displayed to the user.
Real-time Streaming Responses
Raif conversations include built-in support for streaming responses, where the LLM’s response is displayed progressively as it’s being generated.
Each time a conversation entry is updated during the streaming response, Raif will call broadcast_replace_to(conversation) (where conversation is the Raif::Conversation associated with the conversation entry).
When using the raif_conversation view helper, it will automatically set up the Turbo Streams subscription for you.
Streaming Chunk Size Configuration
By default, Raif will update the conversation entry’s associated Raif::ModelCompletion and call broadcast_replace_to(conversation) after 25 characters have been accumulated from the streaming response. If you want this to happen more or less frequently, you can change the streaming_chunk_size configuration option in your initializer:
Raif.configure do |config|
config.streaming_chunk_size = 100
end
Limiting Conversation History
For long-running conversations, the full conversation history can grow quite large, leading to higher API costs, context window limits, and slower responses.
Raif provides llm_messages_max_length to limit how many conversation entries are sent to the LLM when processing the next entry. This can help you keep costs predictable and stay within context window limits.
Global Configuration
Set a default limit for all conversations in your initializer:
Raif.configure do |config|
# Limit to the last 50 conversation entries (default)
config.conversation_llm_messages_max_length_default = 50
# Or set to nil to include all entries
config.conversation_llm_messages_max_length_default = nil
end
Per-Conversation Configuration
Override the limit for specific conversations:
# Limit to last 20 entries for this conversation
conversation = Raif::Conversation.create(
creator: current_user,
llm_messages_max_length: 20
)
# Or remove the limit entirely for this conversation
conversation.update(llm_messages_max_length: nil)
Read next: Agents